Explain AGIL model. the first letters of the four functions he devised as A – adaptation; G – goal attainment; I – integration and L – latency (pattern maintenance – tension management).

In collaboration with
Robert Bales and Edward Shils, Parsons published a book named “Working papers
in the Theory of Action” shortly after “The Social System” in 1953, which was
presented as his yet another theoretical extension of his previous scheme of
analysis. A function is “a complex of activities directed towards meeting a
need or needs of the system”. Thus, building on ideas in “the social system” as
well as on the results of small-group research previously conducted by Bales,
Parsons and his collaborators now suggested that all action systems were faced
with four major survival problems or requisites if they were to survive and
develop, those are adaptation; goal attainment; integration and latency. This
idea which he developed, have been referred variously as the “system problems”,
the “functional imperatives”, the “four-function paradigm”, or the famously
called “AGIL model”, based on the first letters of the four functions he
devised as A – adaptation; G – goal attainment; I – integration and L – latency
(pattern maintenance – tension management).
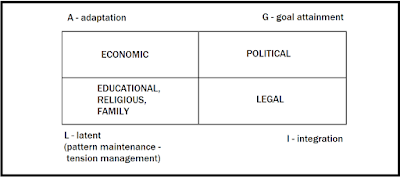 |
| The four functional system problems represented by AGIL model |
In the context of the
social system, Parsons usually pictures society or the social system as a large
square that is (further) divided into four equal parts by him. These parts are
the four functional system problems, represented by the letters AGIL as –
ADAPTATION
– It involves the problem of securing from the environment sufficient
facilities and then distributing these facilities throughout the system. In
this a system must cope with external situational exigencies. Social
institutions are interrelated systems of social norms and roles that satisfy
social needs or functions and help solve social system problems. It is
fulfilled by those structures that help a system to adapt to its environment.
Adaptation draws in resources from the environment and converts them to usable
elements and distributes them throughout the system. For an example of social
institution is the economy, if it is to survive, a social system needs certain
structures or institutions that will perform the function of adaptation to the
environment.
GOAL ATTAINMENT –
It refers to the problem of establishing priorities among system goals and
mobilizing system resources for their attainment. This is the subsystem that
activates and guides all the other elements toward a specific goal. Example,
government.
INTEGRATION
– It denotes the problem of coordinating and maintaining viable
interrelationships among system units by having mechanism for integration.
Parsons meant by integration, the need to coordinate, adjust and regulate
relationships among various actors or units within the system, thus preventing
mutual interference, in order to keep the system functioning. In society, the
structure most responsible for this overt coordination is the legal system.
LATENCY
– Latency embraces two related problems: pattern maintenance and tension
management.
 |
| AGIL |
The first fold pertains
to the problem of how to insure that actors in the social system display the
appropriate characteristics (motives, needs, role-playing skills and so forth).
While the second fold is concerned with the problem of dealing with the
internal tensions and strains of actors in the social system. This problem is
one of keeping the value system intact and guaranteeing the conformity of the
members of the system by transmitting societal values and by invoking value
commitment. The chief socializing agents in society are the structures that
meet the requirement of latency are religion, education, and family.
All of these requisites
were implicit in “The Social System”, but they tended to be viewed under the
general problem of integration. In Parsons’ discussion of integration within
and between action systems, problems of securing facilities (adaptation),
allocation and goal seeking (goal attainment), socialization and social control
(latency) were conspicuous. Thus, the development of the four functional
requisites – abbreviated A,G,I, and L – is not so much a radical departure from
earlier works but an elaboration of concepts implicit in “The Social System”.
However, with the
introduction of A, G, I, L, there is a subtle shift away from the analysis of
structures to the analysis of functions. Structures are now viewed explicitly
in terms of their functional consequences for meeting the four requisites.
Interrelationships among specific structures are now analyzed in terms of how
their interchanges affect the requisites that each must meet.
 |
| Parsons' Functional Imperativism or Requisite Functionalism |
As Parsons’ conceptual
scheme became increasingly oriented to function, social systems are divided
into sectors, each corresponding to a functional requisite – that is, A, G, I,
or L. in turn, any subsystem can be divided into these four functional sectors.
And then, each of these subsystems can be divided into four functional sectors,
and so on. Each system, therefore, develops four specialist subsystems in the
process of meeting these requirements. This process is named as “functional
sectorization”, which is given by Jonathan H. Turner.
 |
| Parsons Functional Imperativist View of Social Systems |
Of critical analytical
importance in this scheme are the interchanges among systems and subsystems. It
is difficult to comprehend the functioning of a designated social system
without examining the interchanges among it’s A, G, I, and L sectors,
especially since these interchanges are affected by exchanges among constituent
subsystems and other systems in the environment. In turn, the functioning of a
designated subsystem cannot be understood without examining internal
interchanges among its adaptive, goal attainment, integrative, and latency
sectors, especially since these interchanges are influenced by exchanges with
other subsystems and the more inclusive system of which it is a subsystem.
___________________________________________________________________
You can visit some significant
Theories by some Great Theorists:
Voluntaristic Theory of Action (Voluntaristic Action), Generalized Media of Exchange, Cynicism (Circulation of Elites), Hierarchy of the Sciences (The Classification of the Science), The Philosophy of Money, Organicism, The Laws of Three Stages, Order and progress (Interrelation between Social Statics and Social Dynamics)
Voluntaristic Theory of Action (Voluntaristic Action), Generalized Media of Exchange, Cynicism (Circulation of Elites), Hierarchy of the Sciences (The Classification of the Science), The Philosophy of Money, Organicism, The Laws of Three Stages, Order and progress (Interrelation between Social Statics and Social Dynamics)
Reference:
- George Ritzer, Sociological Theory.
- Jonathan H. Turner, The Structure of Sociological Theory.
- Kenneth Allan, Contemporary Social and Sociological Theory.
- Ruth A. Wallace and Alison Wolf, Contemporary Sociological Theory.
___________________________________________________________________
Related Questions:
Parsons' concept and design to understand the AGIL model.
Explanation of Parsons' Functional Imperativist View of Social Systems.
Illustration of four different functional system along with their problems supported by AGIL model.
Aptitude Amplifier ©2017. All Rights Reserved.










![Validate my RSS feed [Valid RSS]](https://www.feedvalidator.org/images/valid-rss-rogers.png)
